- The mRNA comes to the cytoplasm, with a starting codon AUG.
- A small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA. The ribosome has two ribosomal units (small and large).
- The first tRNA carrying a specific amino acid, met, at one end and having a specific nucleotide triplet, anticodon, UAC, at the other end comes to bind to the starting codon.
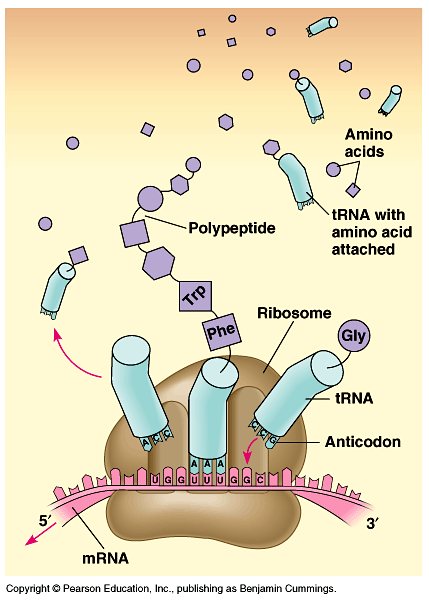
- The ribosome also has one site for binding of mRNA and three sites for the binding of tRNA (P site, A site, E site).
- A site: new tRNA with next amino acid to be added to the chain.
- P site: holds growing polypeptide chain.
- E site: discharged tRNA which will return to cytoplasm and pick up designated amino acid.
- Initiation factors brings the large ribosomal subunit to mRNA, placing the tRNA in the P site.
Act II: Elongation
- Another tRNA carrying amino acid recognizes its corresponding codon at the A site.
- An RNA molecule catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the polypeptide in the P site with the new amino acid in the A site.
- The polypeptide chain is transferred to the tRNA at the A site.
- The ribosome moves the tRNA with the attached polypeptide from the A site to the P site. This process need energy provided by GTP.
- The first tRNA enters the E site, and as the third tRNA attaches to the A site, it exits the E site to the cytoplasm to pick another amino acid.
Act III: Termination
- When one of the three stop codons UAG, UAA, UGA reaches the A site, a release factor cut the bond between the polypeptide chain and its tRNA at the P site.
- Polypeptide, which is known as protein, is released.
- Translation complex disassembles.


No comments:
Post a Comment